IP TRANSIT SERVICES
Connect to our service in or outside of your existing footprint and experience a scalable IP solution for your business. With a mission to deliver maximum performance, we offer IPv4 and IPv6 internet connectivity built for performance, reliability, and scalability. Clients can take advantage of Colocation America’s IP Transit Services by either collocating their server in one of our secure data centers and/or leasing a dedicated server from us. No matter your IT infrastructure needs, you will receive direct connections to our top notch network infrastructure partners. With connection speeds starting from 100 Mbps up to 10 Gbps, all on your very own dedicated uplink, your company will get connected to clients and employees faster than ever before. With 22 data center locations, get the connection speeds your business needs wherever you call home!
What Is IP Transit?
IP transit is much what you would expect. It’s a way for one IP address to get to another IP address, or to go from an Internet Service Provider (ISP), or an IP Service Providers, to the larger framework of the internet not under the ISP’s control. Colocation America’s high-speed IP address service (IP Transit) provides you with low latency and fewer hops which will get you where you need to go—fast!
All of our IP Services are backed by a 100% Network Uptime Guarantee and include:
- 24/7/365 Network Monitoring
- Carrier Neutral Hosting
- Full BGP Support to 300+ bandwidth providers
- Direct cross-connections to any providers with direct access to One Wilshire
- Large and Small blocks fit network needs
- Aggregate 95th percentile billing
Colocation America has all the network speed and availability you could ever want, along with top of the line nodes, hops, and ranges you need to run your business successfully.
What Is an Internet Protocol (IP) Address?
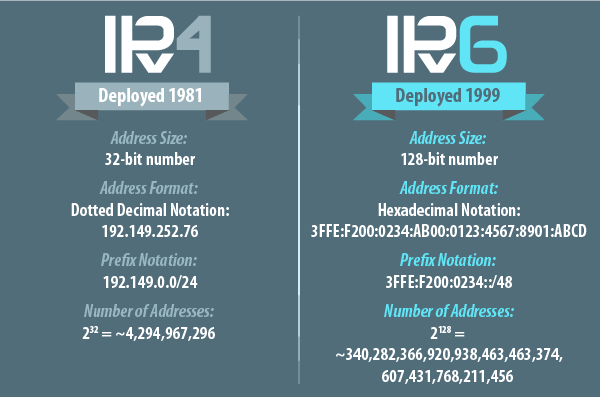
Internet Protocol, or IP, is an internet protocol network used by private and public networks to facilitate communication between devices within the network. All types of network, from the World Wide Web to small private network, depend on assigned IP addresses to dictate where information goes. An IP address is set of unique 8-bit numbers assigned to a device that connect to a network. In other words, your IP address is like your home address but for internet-capable devices. Instead of “mailing” a letter, you’re “mailing” information. There are two types of IP addressing standards, IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is the most widely used and familiar type of IP address, but with IPv4 address space running out, IPv6 is in line to replace it in the future.
What Is the Border Gateway Protocol?
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is defined by Cisco as “an inter-autonomous system routing protocol.” In layman’s words, the BGP exchanges local routing information between different Internet Service Providers (ISPs)—for example: Comcast and Time Warner. Boiled down even further, the Internet is a gigantic place—a network of networks. The BGP ideally acts as the Internet’s GPS (enough initialisms for you yet?) sending your request to its desired location. For example:
- You’re on your computer and you want to watch some Netflix
- You type in netflix.com into your browser’s search bar
- It looks up the address for Netflix
- It then pushes the address to your router which goes and finds Netflix
- Your router sends the request to the next router which checks the routing tables (mentioned above)
- Through the tables it sees that Netflix is over there, and you can go out this router here to get there
- Your request follows that route and hits the next router on another network
- This new router agrees that Netflix is “over there” and says that you need to go to that router at Netflix’s data center
- Netflix’s router gets you to their servers and they send the information you requested back to you in much the same manner.
- Bonus: if one of those routers is down / flooded the tables will show your request an alternate route to get there.
What Is IP Traceroute?
An IP traceroute is typically used to diagnose where the problem is when one is trying to connect to the webpage and/or their internet is running slowly. Just take a look at the amount of diagnostic syntax one can use to get exactly the information they need:
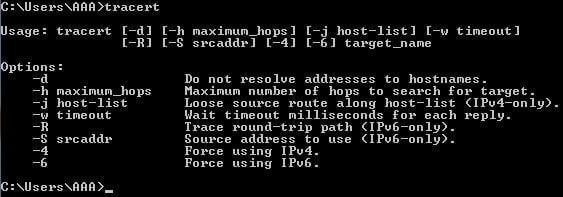
Thus, performing a traceroute will give you a detailed look at the route a packet takes as it travels from one network system to another.